Art Concept: Analogous Colors. Artists often use colors that are analogous. “Analogous” means near. Analogous colors mean two or more colors that are side by side on the color wheel and often contain the same primary color (green, yellow, orange). Analogous color schemes often produce a strong “mood.”
Teaching ideas: Show students the color wheel. Analogous colors schemes are like different pieces of pie – some are big, some are small. Have students arrange crayons in a color wheel. First have them remove blacks, whites and browns. Start by making a triangle with red, yellow and blue, then add orange, purple and green and then other colors if they want. Then show them the images below. In each work of art, have the students identify where the analogous colors fit into the color wheel (i.e. green through yellow to orange, or blue to purple, etc.) and whether the piece of analogous pie is big or small. Note that sometimes an artist may use a complement to the one of the analogous colors to make some object stand out. Ask them if the different analogous schemes produce clear feelings in the paintings.
Book: Hop Jump, by Ellen Stoll Walsh (illustrations are in yellow to blue analogous colors.) Many book illustrations might be used.

Orange and Yellow Rothko (American), 1956. orange/yellow

The Garden, Morisot (French), 1883. yellow/green/blue
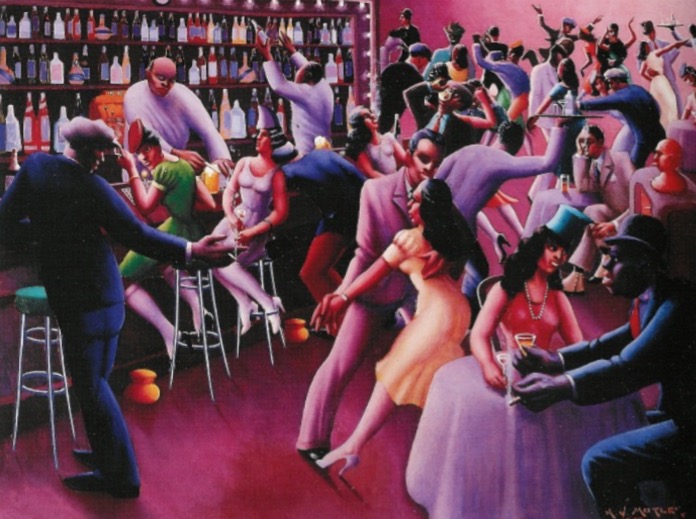

Nightlife, Archibald Motley Jr. (American), 1943. red/purple/blue/green (orange accidentals)

Water Lillies, Monet (French), 1906. purple/blue/green (red compliment accent)

Shah Jahan & Dara Govardhan (Indian), 1657. green/yellow

Russian Beauty in Landscape, Kandinsky (Russian), 1904. green/blue/purple
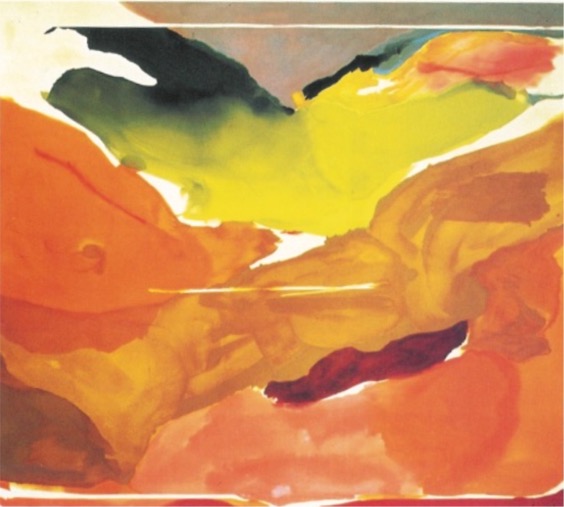

Nature Abhores a Vacuum, Helen Frankenthaler (American), 1973. green/yellow/orange/red

Mihrab unit from masjid, Mayden Kashan (Islam, middle east), 1226. green/blue/purple
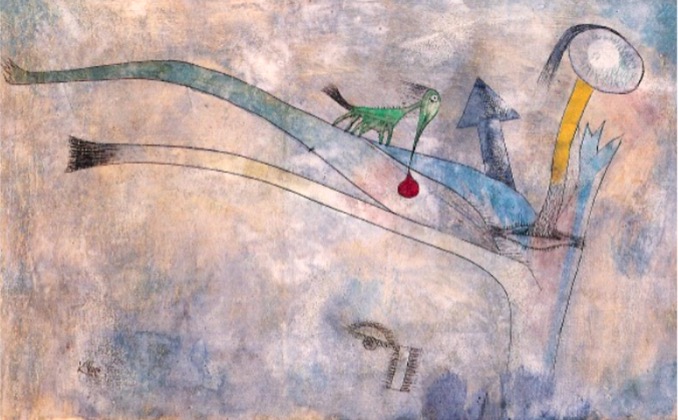

Grune pflanzan blut laus, Klee, 1924. yellow/green/blue (red accidental)
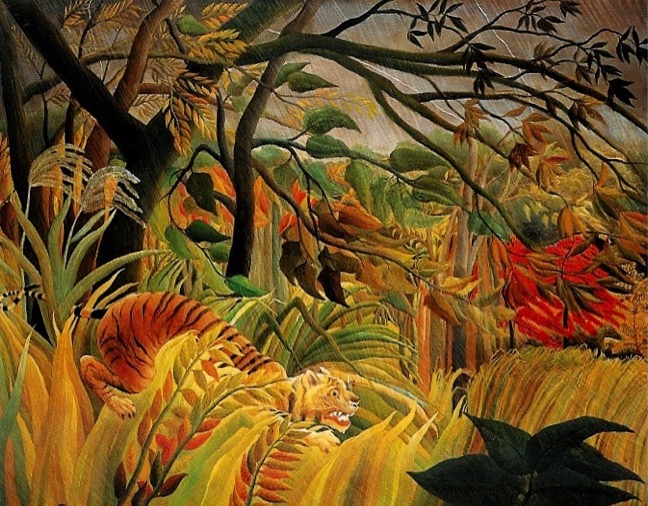

Tropical Storm with Tiger, Rousseau (French), 1891. red/orange/yellow/green

Girl with Sunflowers, Diego Rivera (Mexican), 1941. orange/yellow/green/blue

Five Women in the Street, Kirchner (German), 1913. yellow/green/blue
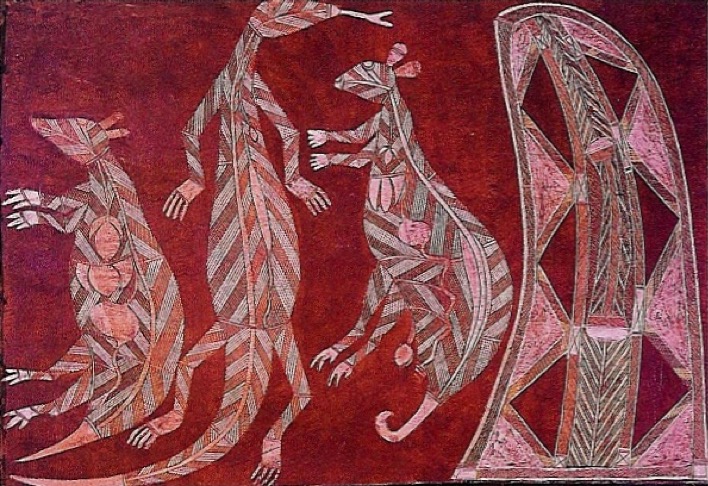

Kangaroos (bark painting), Aboriginal 20thC. red/purple

Sumerian Gate Guard, 404-358 BC. green/yellow/orange
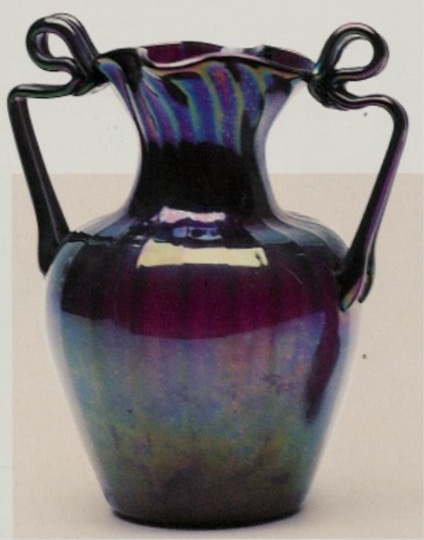

Vase, Guiseppe Barovier,1875. green/blue/violet
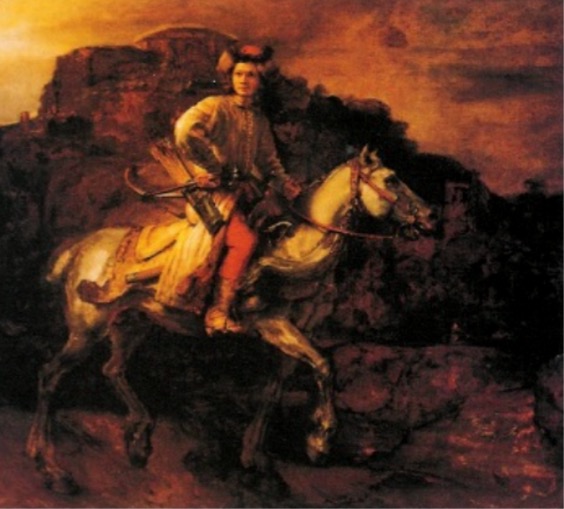

Polish Rider, Rembrandt (Dutch), 1655. red/orange/yellow

Chartes Cathedral, Corot (French), 1830. yellow/green/blue

Yellow Dancers, Degas (French), 1876. yellow/green (complimentary color red accent
Fueling Success for Every Student, Every School