Please note: Resources and lesson plans provided here are intended for non-profit use only. Use of these materials for commercial purposes should give attribution to the Issaquah Schools Foundation and be accompanied by a nominal donation at www.isfdn.org/donate. Thank you.
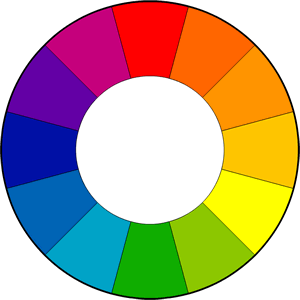
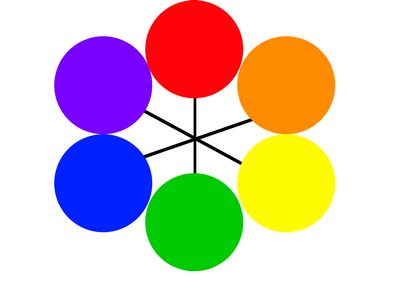
Color Wheel: a circle with different colored sectors used to show the relationship between colors.
Primary Colors: red, yellow and blue. The colors from which all other colors are created by mixing.
Secondary Colors: green, orange and purple. Colors created by mixing primary colors only.
Intermediate Color: a color created by mixing a primary color with the secondary color next to it; also called a tertiary color; intermediate colors include red-orange, yellow-orange, yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and red-violet.
Analogous Colors: Colors that appear next to each other on the color wheel. For example, red, orange, and yellow are analogous colors. If mixed, these colors tend to make variations of the original colors.
Complimentary Colors: Colors that appear opposite to one another on the color wheel. These colors compliment one another and are often used together in order to create a strong visual impact (one example is the UW Husky colors). Sometimes also called contrasting colors. If mixed, complimentary colors tend to create "muddy" tones such as black, brown, or gray.
Red - Green
.png)
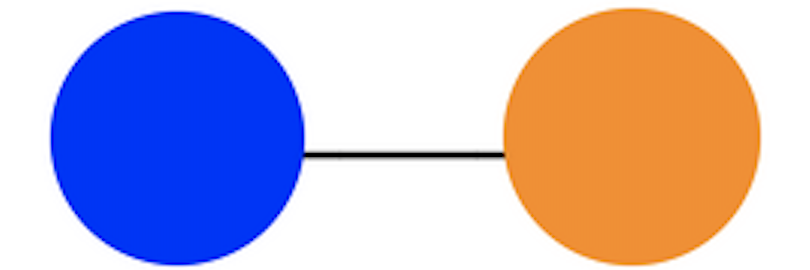
Blue -Orange
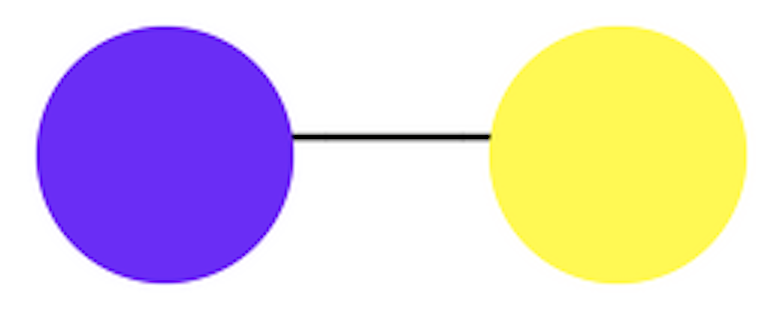
Purple - Yellow
Warm Colors: a group of colors on the color wheel that are associated with warmth, such as red, yellow, and orange (and variations on these colors such as pink, red-orange, etc.). In art, warm colors appear to advance toward the viewer.

Cool Colors: a group of colors on the color wheel that includes blues, greens, and violets. In artwork, cool colors appear to be farther away from the viewer.

Mouse Paint book by Ellen Stohl Walsh.
Printable Color Wheel Worksheet (blank for students to complete).
Please note: Resources and lesson plans provided here are intended for non-profit use only. Use of these materials for commercial purposes should give attribution to the Issaquah Schools Foundation and be accompanied by a nominal donation at www.isfdn.org/donate. Thank you.
Fueling Success for Every Student, Every School